#Usability Studies
#Interviews
#Competitive Analysis
Interviews
Open Card Sorting
Design Fiction
Usability Testing
Key Learnings
Interviews
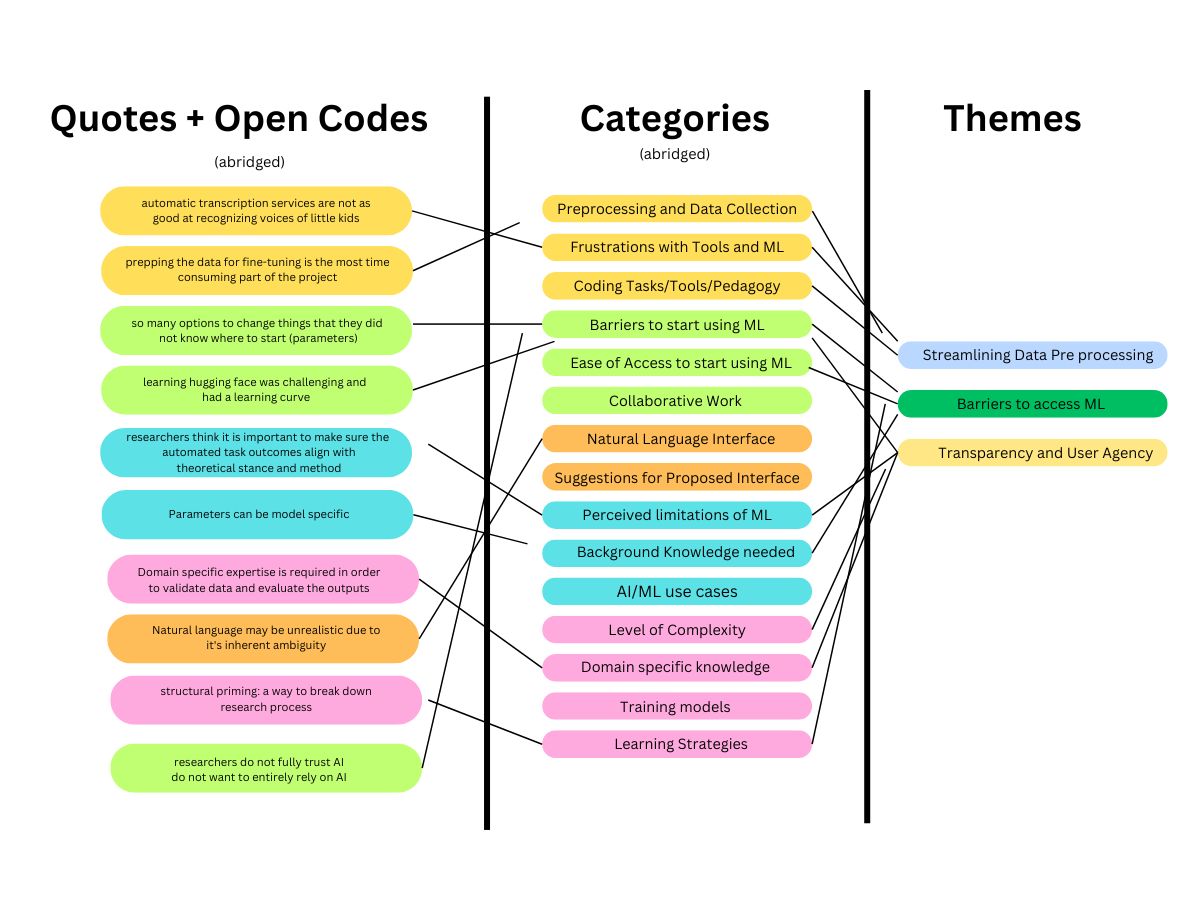
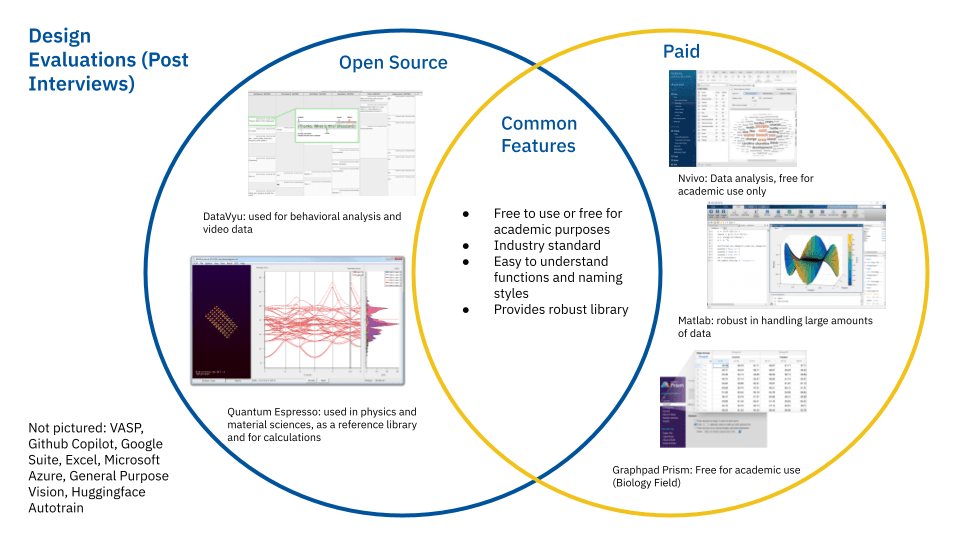
We conducted 14 interviews across 10 subject disciplines with machine learning scientists, conversation designers, as well as PhD researchers. Through these interviews, we explored any existing tools they already used to handle data, and discussed at length their current frustrations with their workflow. Through these interviews, we uncovered three main themes to our research questions.
There is a high entry point to get into ML.
People don’t understand AI suggestions. There are hesitancies to incorporate model outputs (i.e. answers you get from ChatGPT) in aiding with research stemming from either intuitive hesitation or experiencing an error using model output
Pre-processing data had a high chance of introducing errors and was tedious to do
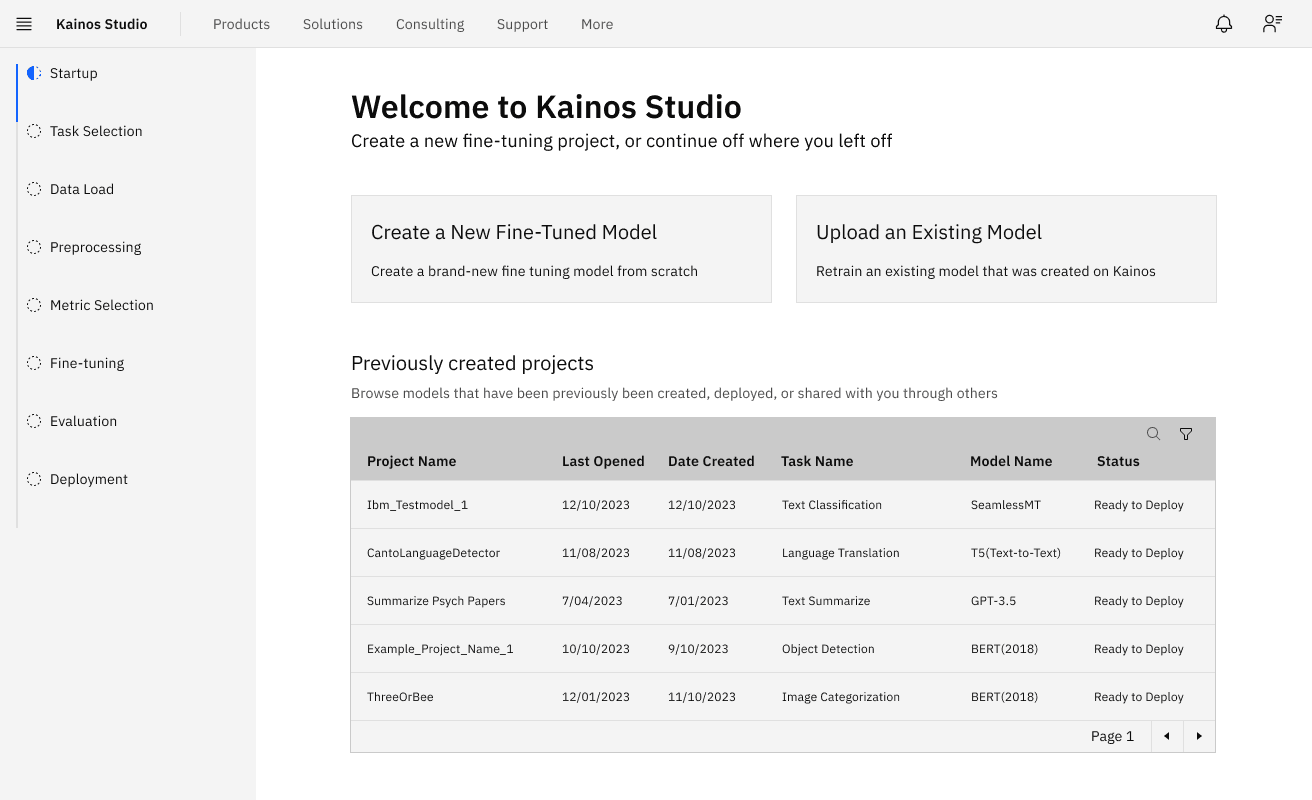
These themes shaped the way we approached designing the prototype. Some recommendations resulting from these themes in our research include: reducing technical jargon, including supporting documentation to walk new users through fine tuning, incorporating explainable AI to demystify the black box in machine learning, and more.
Design Fiction
We created a worksheet that prompted our participants to personify an AI-assisted tool they were familiar with. This allowed us insights into their attitudes towards using AI-tools and their level of trust in its performance. Users generally had a positive outlook on tools, however, tools that were corrective in nature had more negative traits attributed to them, such as being "judgemental, know-it-all".
Open Card Sort
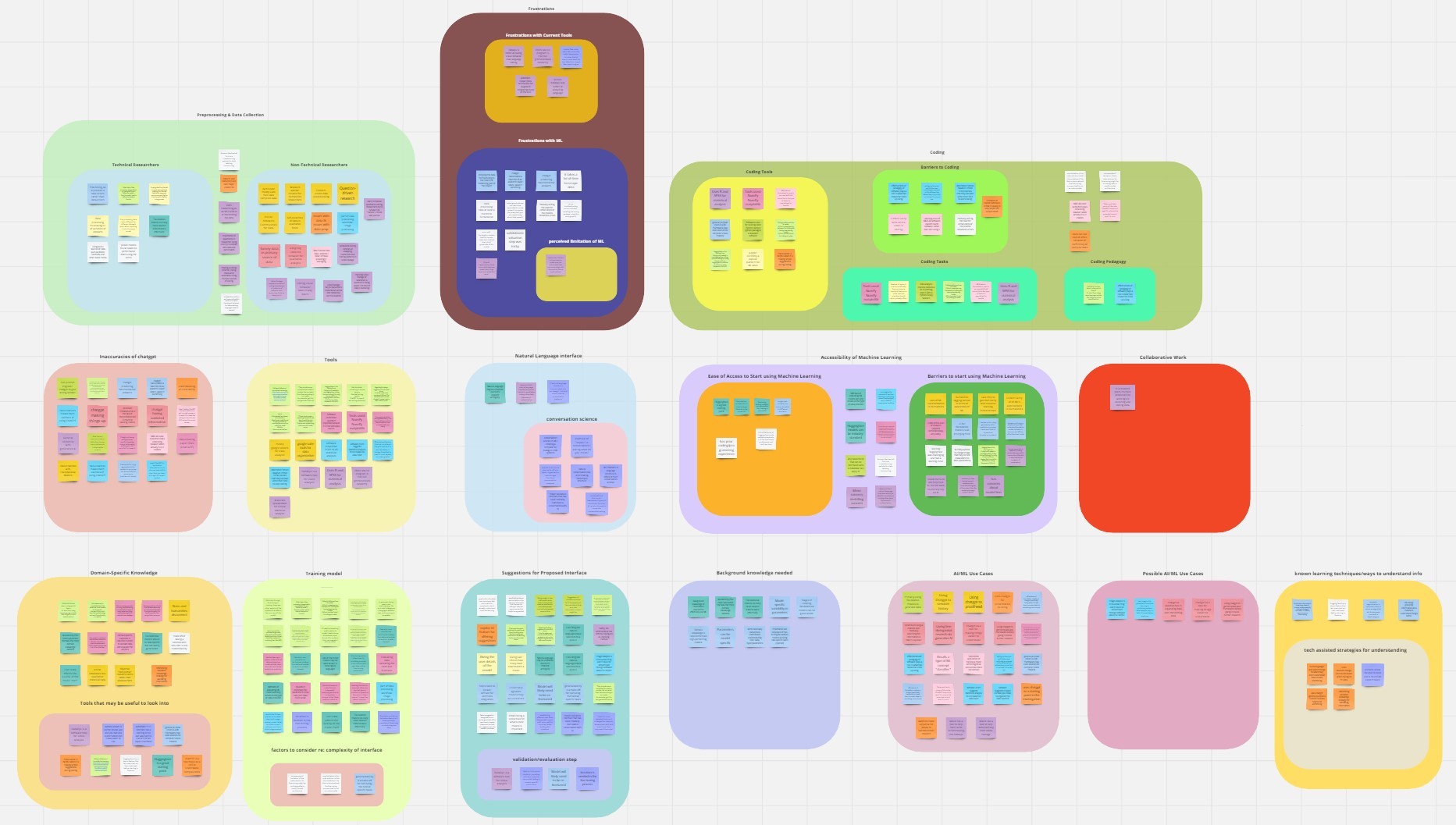
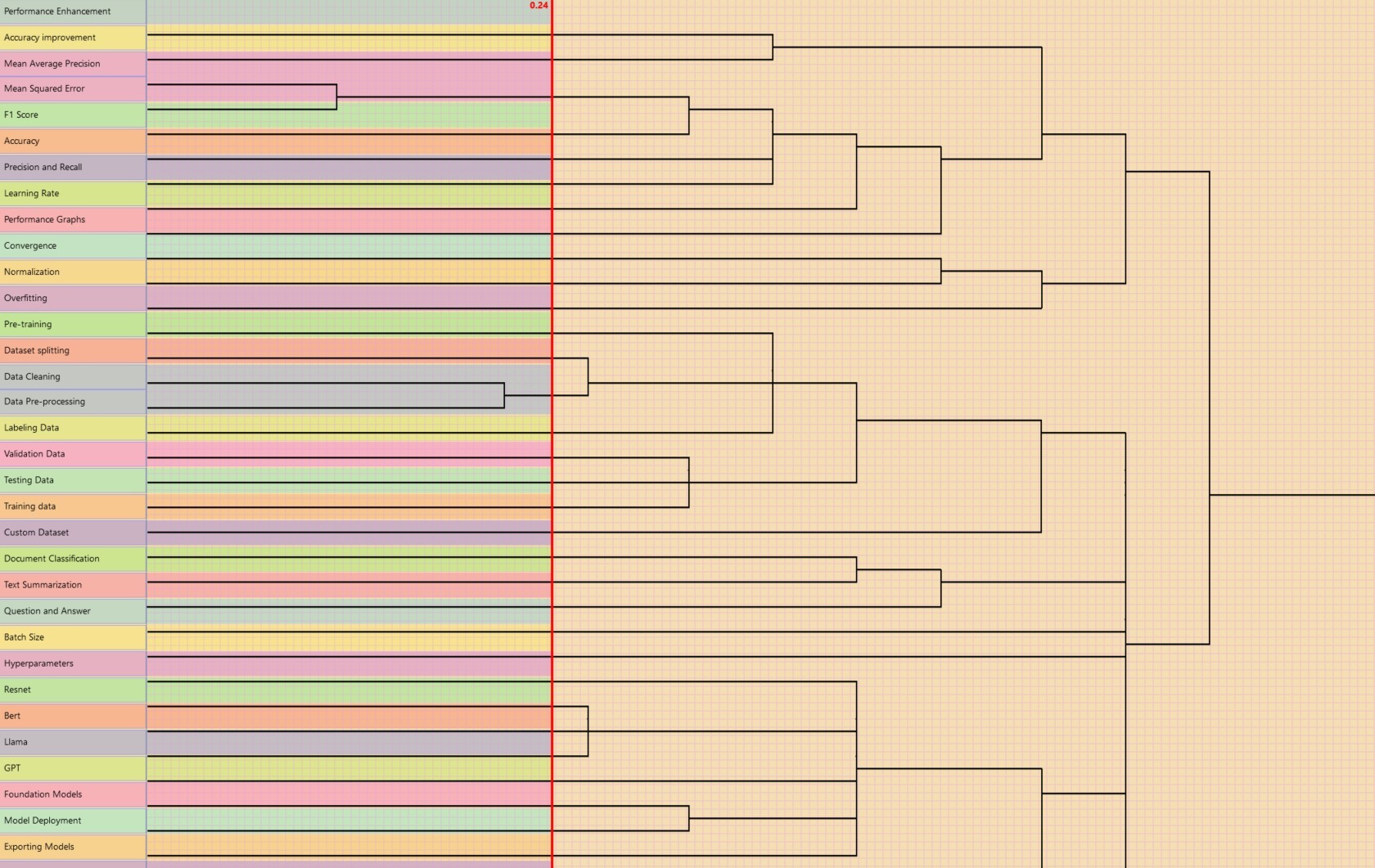
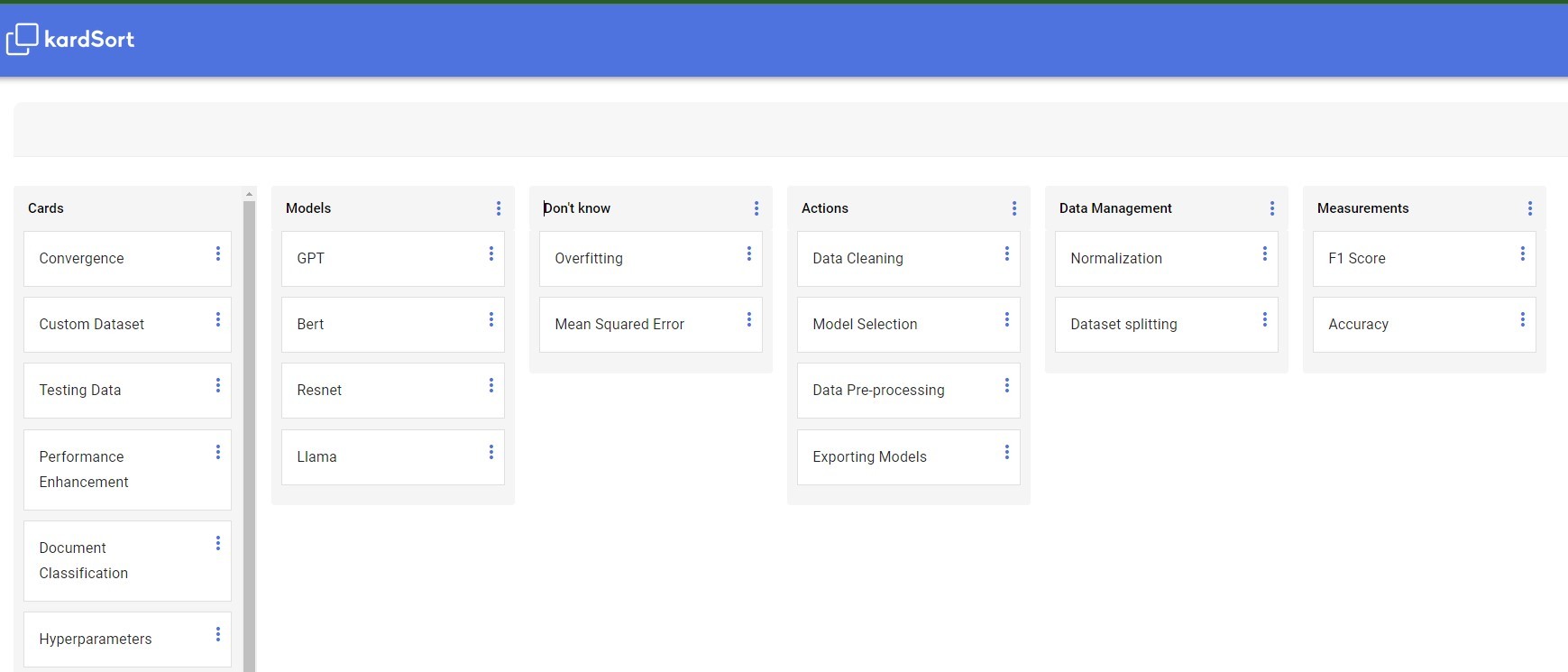
We conducted an open card sort study with 32 total terms and generated 190 categories in all. During the design phase of this project, we wanted to understand what kind of information non-technical users might be less intuitive to understand and would need more support with on the platform. Results from the single link clustering analysis shows users typically are adept at understanding what are fine tuning tasks and data handling actions, but would need more support in understanding the names and functions of specific foundation models as well as evaluation metrics.
Note:
These were some highlights of our research process, for more insights and details please reach out to me via email at hello@naomidu.com
Reflection
This project challenged us to immerse ourselves in a topic we weren't familiar with at the start of the work, and gave us an opportunity to center our participants as experts. If given a chance to expand on this work, it would be great to conduct usability studies from a traditional accessibility standpoint.